Emails are one of the most important means of communication in everyday business and medical practice. But without encryption, emails are as secure as a postcard – anyone with access to the connection can read them or manipulate them while in transit. Secure communication is essential, especially in professional and medical environments, where confidential information such as contracts, financial data, patient data, or personal information is exchanged.
This is where S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) comes in. This proven encryption technology protects emails, ensures their authenticity, and prevents tampering. But how exactly does S/MIME work, and what possibilities does this encryption offer in practice?

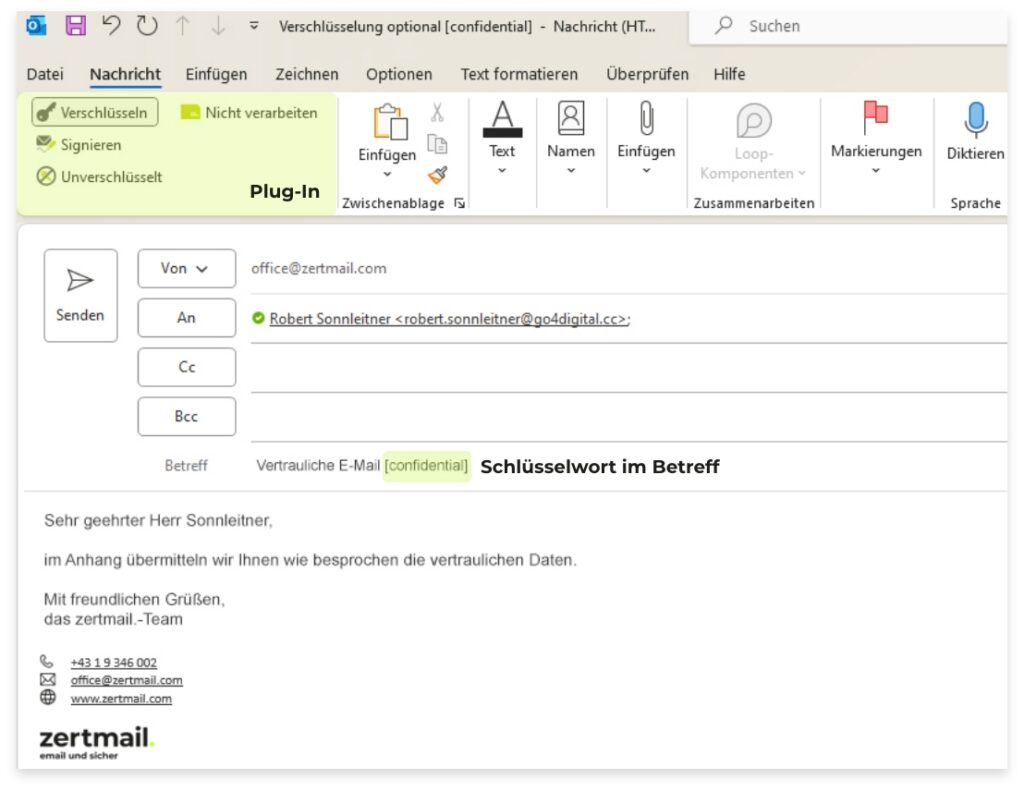

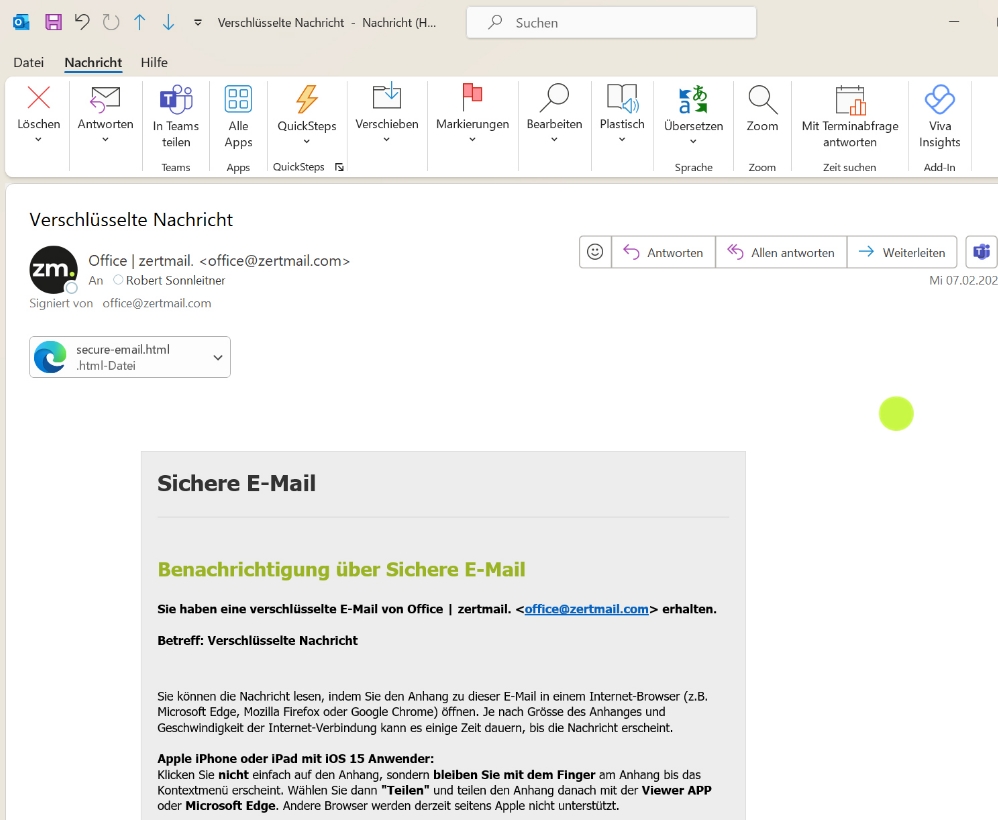

What is S/MIME?
S/MIME is a widely used standard for end-to-end encryption and digital signatures of emails. The method uses asymmetric cryptography to encrypt messages and confirm the sender’s identity. The two main functions of S/MIME:- Email encryption: The message is encrypted so that only the intended recipient can decrypt it.
- Digital signature: The email is provided with a signature that confirms the sender’s authenticity and detects tampering.

How does S/MIME work technically?
S/MIME is based on a certificate system with two keys:- Public key: Used to encrypt emails. It is accessible to everyone.
- Private key: Used to decrypt encrypted messages. Only the recipient has access to it.
This is how encryption with S/MIME works:
- The sender uses the recipient’s public key to encrypt the email.
- The encrypted message can only be decrypted by the recipient using their private key.
- Even if an email is intercepted during transmission, the content remains unreadable thanks to the encryption.

This is how digital signatures work with S/MIME:
- The sender signs the email with their private key.
- The recipient can verify the signature with the sender’s public key.
- This ensures that the message is authentic and has not been subsequently altered.

Advantages of S/MIME encryption:
High security through end-to-end encryption S/MIME ensures that only the intended recipient can read the message. Even hackers or malicious third parties who intercept the email in transit have no way to decrypt the content. Protection against manipulation and phishing The digital signature ensures that the message truly originates from the sender and has not been altered in transit. This protects against forged emails and man-in-the-middle attacks. Easy integration into common email programs Many email clients support S/MIME by default, so no additional software is required. After a one-time setup, encryption runs in the background without any further manual configuration. Compliance with legal regulations (GDPR, NIS-2, GtelG) Companies and medical institutions are obligated to protect sensitive data. The GDPR, the NIS-2 Directive, and the GtelG require the protection of personal data, especially in business and medical email communications. S/MIME helps to easily implement these requirements.
Conclusion: Why S/MIME is the best choice for secure emails
S/MIME is an international standard and one of the most secure and widely used methods for email encryption and digital signatures. By using asymmetric cryptography, S/MIME ensures that your emails remain confidential and cannot be tampered with. Providers like zertmail. enable particularly easy implementation of S/MIME. After a one-time setup, certificates are automatically renewed, requiring no further administrative support. Use S/MIME encryption with zertmail. to communicate in compliance with GDPR, NIS-2, and the German Telecommunications Act (GtelG) – simply, securely, and effortlessly. Would you like to finally make your email communication secure? Then zertmail is the right solution for your company. 👉 Contact us now! Are you an IT service provider or do you serve customers with high data protection needs? Become a zertmail. partner and benefit from special conditions: 👉 Learn more & become a partner